Working Brain
Brain anatomy
Search CIDPUSA WEBSITE
😏
AUTOIMMUNE EPIDEMICFriday, 24 June 2005
Nervous System Brain
Contents
Neurons and NervesNeurotransmitter
The Brain
Spinal Cord
Peripheral Nervous System
Autonomic Nervous System
Senses: Sight,Senses, Smell,Taste, Sences,Senses
Memory
Higher Functions
Altered States
| Structure | Location | Functions |
|---|---|---|
| Thalamus | in the middle of the limbic system | relays incoming information (except smell) to the appropriate part of the brain for further processing. |
| Hypothalamus, Pituitary Gland | beneath thalamus | regulates basic biological drives, hormonal levels, sexual behavior, and controls autonomic functions such as hunger, thirst, and body temperature. |
| Optic Chiasm | in front of the pituitary gland | left-right optic nerves cross-over point. |
| Septum | adjacent to hypothalamus | stimulates sexual pleasure |
| Hippocampus | within the temporal lobe | mediates learning and memory formation. |
| Amygdala | in front of the hippocampus | responsible for anxiety, emotion, and fear |
| Mammillary Body, Fornix | linked to the hippocampus | have a role in emotional behavior, learning, and motivation. |
| Caudate Nucleus, Putamen, Globus Pallidus,Basal Ganglia (Striatum) | outside the thalamus | involves in movement, emotions, planning and in integrating sensory information |
| Ventricles and Central Canal | from tiny central canal within the spinal cord to the enlarged hollows within the skull called ventricles | fills with cerebrospinal fluid for mechanical protection. |
| Cingulate Gyrus | above corpus callosum | concentrates attention on adverse internal stimuli such as pain, contains the feeling of self. |
| Corpus Callosum | under the cingulate gyrus | is a bundle of nerve fibers linking the cerebral hemispheres, involve in language learning. |
| Forebrain (Human Brain) | ||
| Frontal Lobe (Conscious Brain) | in front of the head | controls voluntary movement, thinking, and feeling. |
| Prefrontal Cortex | in front of the frontal lobe | inhibits inappropriate actions, forms plans and concepts, helps focus attention, and bestows meaning to perceptions. |
| Parietal Lobe | in top rear of the head | contains the primary somatosensory area that manages skin sensation. |
| Occipital Lobe | in the back of the head | contains the visual cortex to manage vision. |
| Temporal Lobe | on each side of the head above the temples | contains the auditory cortex to manage hearing and speech. |
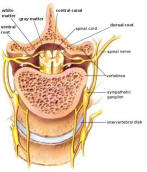
The spinal cord (Figure 04a) lies along the
middorsal line of the body. It has two main functions: (1)
it is the center for many reflex actions, and (2) it
provides a means of commu-nication between the brain and the
spinal nerves that leave the cord (Figure 04b). The white
matter of the cord is white because it contains myelinated
long fibers of interneurons that run to-gether in bundles
call tracts. These tracts connect the cord to the brain. The
dorsal ones are primarily ascending to the brain, while the
ventral tracts bring information down from the brain. The
inner portion of the
Figure 04a Spinal Cord
[view large image]
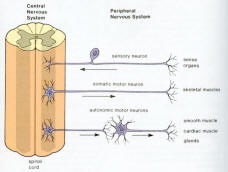
Figure 04b CNS and PNS
[view large image]
cord is filled with a mass of nerve cell bodies called gray matter. Each spinal nerve emerges from the spinal cord as two short branches, the dorsal and the ventral roots. These roots join just before the nerve leaves the vertebral column.
Peripheral Nervous System
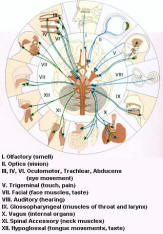
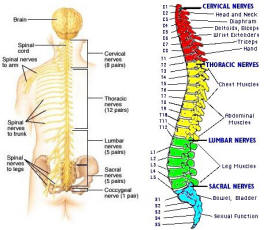
The peripheral nervous system is outside the CNS. It consists of the various nerves that connect particular parts of the CNS with particular organs. Humans have 12 pairs of cranial nerves and 31 pairs of spinal nerves. Cranial nerves (Figure 05) are either sensory nerves, motor nerves, or mixed nerves. All of them, except the vagus nerve, control the head, the face, the neck, and the shoulders. The vagus nerve controls the internal organs. Table 03 lists the functions of the various cranial nerves. All spinal nerves (Figure 06) are mixed nerves that take impulses to and from the spinal cord. Table 04
Figure 05 Cranial Nerves [view large image]
Figure 06 Spinal Nerves
[view large image]
heart rate, breathing rate, aortic blood pressure