Neurology Anatomy Physiology
December 14, 2021
Contents
neurons and Nervesneurotransmitter
The Brain & Spinal Cord
Cranial Nerves
Peripheral Nervous System
Autonomic Nervous System
Senses: Eye diagrams, Hearing, Smell, Taste, Taste & Tongue Sensation, Balance
Memory , Memory types, Creation of Memory
Higher Functions
Altered States
Memory
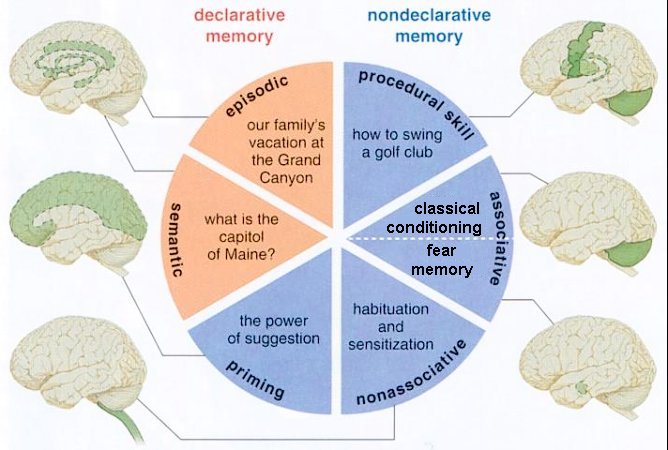
Figure 24a Memory Classification
[view large image]
 |
There are many ways to classify the memory. The concept of explicit and implicit memory refers to whether or not the recollection is produced consciously and intentionally. While the scheme of declarative and nondeclarative memory depend on the retrieval that can be declared verbally or not. Associative memory is triggered by clues; nonassociative memory can be habitual or sensitive. There are also short term and long term memory. One of the classification schemes is shown in Figure 24a. Table 06 is an attempt to put them all together. In the table, the declarative, and the procedural memory are explicit with the rest of nondeclarative memories being implicit. Only the working memory belongs to the category of short term memory fading away in hours, while the others are long term, and available for retrieval in years. Figure 24b shows the components, |
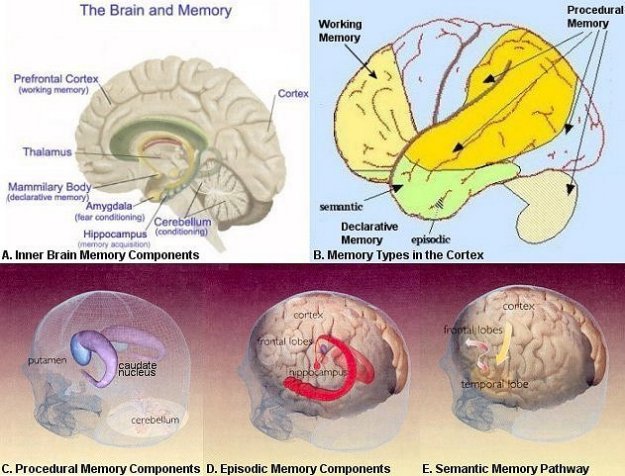
Figure 24b Types of Memory
|
locations, and pathways for many types of
memory. |
| Type | Location(s) | Function | Example(s) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Working Memory | |||
| Phonological Loop | Left hemisphere | Rehearsing verbal information to keep it in the short-term memory | String of numerals and alphabets such as telephone numbers |
| Visual-spatial Scratch Pad | Visual Cortex | Controlling visual imagery | Scanning text |
| Central Executive | Frontal lobe | Controlling awareness of the information in working memory | Constructing sentence, comprehending speech |
| Non-declarative Memory | |||
| Procedural Memory | Cerebellum, temporal lobes | Managing "how to" | Riding a bicycle, kungfu exercise |
| Classical Conditioning | Cerebellum | Forming habitual behaviour | Coffee break, afternoon tea |
| Fear Memory | Amygdala | Emotional conditioning | Phobias, flashbacks |
| Nonassociative Memory | Spinal cord | Habituation and Sensitization | Decreased or increased responsiveness to stimulus |
| Remote Memory (Priming) | Scattered around the cortex | Foundation for new memories | Childhood memory |
| Declarative Memory | |||
| Episodic Memory | Cortex | Remembering past experience | Some enchanted evening |
| Semantic Memory | Frontal lobe, temporal lobe | Registering facts | Meanings of words and symbols |
Table 06 Types of Memory
Powered by cidpusa.org