autoimmune
😏cidpusa.orgSearch Cidpusa web
God Our Guide
Main Links Cidpusa.org
Home pageOverview
Temporal arteritis, is known as giant cell arteritis, it is an autoimmune inflammatory condition affecting the medium-sized blood vessels that supply the head, eyes, and optic nerves. The disease usually affects people over age of sixty and causes the vessels in the temple and scalp to become painful tender and swollen. Women are approximately 4 times more likely to suffer from this disease then men.
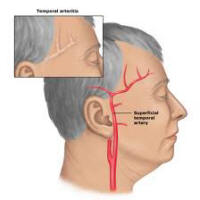
The major concern with temporal arteritis is vision loss, although if allowed to progress, it may affect arteries in other areas of the body. This condition is potentially vision threatening, however, if treated promptly, permanent vision loss can be prevented. Vision is threatened when the inflamed arteries obstruct blood flow to the eyes andoptic nerves. If untreated, permanent vision loss can occur from oxygen deprivation to the retina and optic nerve.
Signs and Symptoms
Patients with temporal arteritis usually notice visual symptoms in one eye at first, but as many as 50% may notice symptoms in the fellow eye within days if the condition is untreated.
Headache, Tenderness of scalp (combing hair may be painful)
Transient blurred vision
Loss of appetite , Fever, Fatigue
Depression, Drooping lid , Double vision
Sore neck, Jaw soreness, especially when chewing food
The disorder may develop along with or after. Giant cell arteritis is almost always seen in people over age 50, but it may sometimes occur in younger people. It is rare in people of African descent. There is some evidence that it runs in families
Detection and Diagnosis
Looking in the Fundus of the EYE
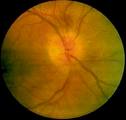 You see a pale disc in the center
You see a pale disc in the center
When temporal arteritis is suspected, the doctor will order blood tests including a erythrocyte (red blood cell) sedimentation rate (ESR) and C-reactive protein test. The ESR test measures the time it takes for the erythrocytes to collect in the bottom of a test tube. The sediment layer of erythrocytes is measured in millimeters and recorded. An abnormally high ESR is indicative of active inflammation.
C-reactive protein is produced in the liver. This protein is released when the body responds to an injury or any other event that signals inflammation. C-reactive protein is measured with a blood test.
A biopsy of the temporal artery is usually recommended. No need to do Biopsy if ESR is elevated just start treatment asap.
inflammation seen on skin Biopsy
The ESR usually is 60-90.
The procedure is performed with local anesthesia. A small section of the temporal artery is removed and examined under magnification for inflammatory cells. This test allows doctors to definitively diagnose temporal arteritis. Cidpusa has many reports of biopsy results which came back negative while the patient had arteritis. This can be seen in burnt out disease where after inflammation atrophy has set in.
Treatment
The ophthalmologist often works in conjunction with the patient's internist to treat this disease. The primary treatment for the disease is oral steroid medication to reduce the inflammatory process. Most patients notice an improvement in their symptoms within several days. In some cases, a long-term maintenance dosage of the steroid is required.Steroid can be given I/V . Monitor with the sed rate the lower it is lower the steroids. Prednisone is preferred starting dose is 40 mg daily orally but consider giving Solumedrol one gram I/V at once and daily for three days.
Patients need to be checked for infections like Mycoplasma, CMV, herpes virus and treated in case of Mycoplasma or as a default antibiotic with Doxycycline. We have seen reversal in three weeks.The antibiotic is based upon CIDPUSA own research and we have seen a faster response to good results.
For detailed management of this disease see this link
😏