Neurotransmitters
December 14, 2021
Contents
neurons and Nervesneurotransmitter
The Brain & Spinal Cord
Cranial Nerves
Peripheral Nervous System
Autonomic Nervous System
Senses: Eye diagrams, Hearing, Smell, Taste, Taste & Tongue Sensation, Balance
Memory , Memory types, Creation of Memory
Higher Functions
Altered States Neurons and Nerve
Neurotransmitters
Neurotransmitters are chemicals that take a nerve signal across the synaptic gap (Figure 02a) between a sending neuron, and a receiving one. On the receiving neuron are receptors into which the neurotransmitters fit like a key in a lock. Once a neuro-transmitter is bound to its specific receptor, the likelihood of the receiving cell "firing" to send its own message is affected. The excitatory neurotransmitter-receptor systems make receiving cells more likely to fire, whereas the inhibitory systems make the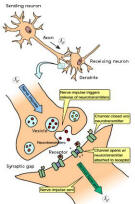
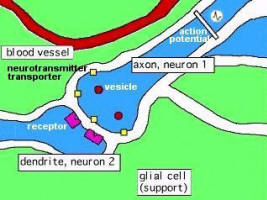 firing less likely (see Figure 29a). It all depends on the type of neurotransmitter. An individual nerve cell can possess both kinds of synaptic connections (with a total of about 50000 synapses on the surface) to other nerve cells. Only if the excitatory charges (positive charge) exceed a threshold does the target neuron starting a nerve impulse of its own and is known as transduction. Figure 02b shows the various components in the synapse. The vesicle contains the neuro-transmitters in the axon. The receptor is located on the surface of the dendrite to pick up the neuro-transmitters. The
firing less likely (see Figure 29a). It all depends on the type of neurotransmitter. An individual nerve cell can possess both kinds of synaptic connections (with a total of about 50000 synapses on the surface) to other nerve cells. Only if the excitatory charges (positive charge) exceed a threshold does the target neuron starting a nerve impulse of its own and is known as transduction. Figure 02b shows the various components in the synapse. The vesicle contains the neuro-transmitters in the axon. The receptor is located on the surface of the dendrite to pick up the neuro-transmitters. The Figure 02a Synapse
[view large image]
Figure 02b Neurotransmitter
[view large image]
transporter is for recycling un-used neutrotransmitters back into the axon; while the glial cell provides nutrition and support for the neurons. - Release - As the action potential comes down the axon, the calcium influx triggers an exocytosis of vesicles that contain the neurotransmitters, which are release into the synaptic cleft.
- Bind - The neurotransmitters then drifts across , binds to the postsynaptic receptors.
- Transduction - Depending on the integration of the excitatory and inhibitory inputs, the receiving dendrite may fire a signal for further transmission.
- Reuptake - The neurotransmitter transporters remove the un-used neutrotransmitters in the synaptic gap back to the axon for re-use. This step is to prevent continuous stimulation of the postsynaptic neuron.
Figure 02c shows the process of signal transmission across the synapse:
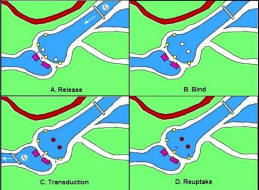
Figure 02c Signal Transmission
[view large image]
There are other ways to turn the signal off. One is simple diffusion into the extracellular space. Another way is to break down the neuro-transmitters with enzymes. Then there are the presynaptic autoreceptors (not shown), which terminate the release once a neutrotransmitter drifts back upstream and hits one of these receptors.Powered by cidpusa.org