CIDPUSA.org Autoimmune diseases
Sensorineural hearingloss ,
Sam J. Marzo, M.D.
Assistant Professor
ENT
Loyola University
Introduction:
The purpose of this paper is to familiarize audiologists with issues related to vertigo and sensorineural hearing loss, and the potential role of intratympanic therapy in treating specific disorders.
The theory behind intratympanic therapy is that by instilling small amounts (<5 cc) of medication into the middle ear, absorption into the inner ear occurs though the round window. The medicine exerts its effect on the ipsilateral cochlear and vestibular end organs.
The benefits of this therapy include; minimal to no systemic side effects, predictable results, and the ability to treat the patients in the clinic or outpatient setting.
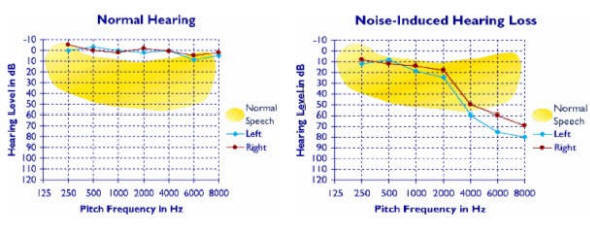
Differential Diagnosis of Vertigo:
Dizziness and vertigo are common disorders. Dizziness can be defined as a sensation of being off balance. Vertigo is more specific and refers to a sensation of movement (usually spinning) of the individual or their surrounding. Dizziness can be secondary to neurological, cardiac, metabolic, psychiatric, vestibular, or other disorders.
Vertigo is usually secondary to dysfunction of the peripheral vestibular system, which includes five paired organs - the horizontal, superior, and posterior semicircular canals - which sense angular acceleration, and the utricle and saccule - which sense horizontal and vertical acceleration, respectively.
Assorted Dizziness Statistics:
1) Dizziness is the most common reasons for a physician visit in patients over age 65 years.
2) Thirty percent of the population will experience vertigo by the age of 65
3) Ninety million Americans will experience dizziness or vertigo during their lives.
Benign Positional Paroxysmal Vertigo (BPPV):
The most common cause of vertigo is Benign Positional Paroxysmal Vertigo (BPPV). This is characterized by a sensation of spinning lasting only several seconds that occurs with quick movements of the head such as rolling over in bed, looking up, or looking down. BPPV is believed to occur secondary to free floating otoconia (calcium carbonate crystals normally within the utricle and saccule) that break loose (spontaneously, or through trauma) and attach to, or cause stimulation of, the posterior semicircular canal with movement of the head. Many cases resolve spontaneously while others are treated with various particle - repositioning maneuvers. Must read celaic disease section once you have read this section.
Please continue to next page for ear disorders If the autoimmune disorder affects the blood, the
person may need blood transfusions. Measures to help with movement or other functions may
be needed for autoimmune disorders that affect the
bones, joints, or muscles. Medicines are often prescribed to control or reduce
the immune system's response. Such medicines may include
corticosteroids and immunosuppressant drugs such as
cyclophosphamide or azathioprine. Before one starts on medication one should find the
offending organism or allergy. The most common are food
allergies and in particular
celicac disease.