Human Brain Parietal eye
brain is an electrochemical organ
See our services section for help and contact information.
continued from the Brain Page of Nervous System
Contents
neurons and Nervesneurotransmitter
The Brain & Spinal Cord
Cranial Nerves
Peripheral Nervous System
Autonomic Nervous System
Senses:Eye diagrams,Hearing,Smell,Taste, Taste & Tongue Sensation,Balance
Memory , Memory types, Creation of Memory,
Higher Functions
Altered States
[Top]
Continued from Brain
Spinal Cord
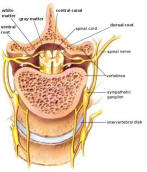
The spinal cord (Figure 04a) lies along the middorsal line of the body. It has two main functions: (1) it is the center for many reflex actions, and (2) it provides a means of commu-nication between the brain and the spinal nerves that leave the cord (Figure 04b). The white matter of the cord is white because it contains myelinated long fibers of interneurons that run to-gether in bundles call tracts. These tracts connect the cord to the brain. The dorsal ones are primarily ascending to the brain, while the ventral tracts bring information down from the brain. The inner portion of the
Figure 04a Spinal Cord
[view large image]
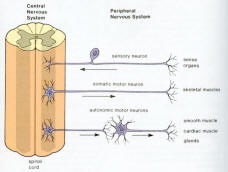
Figure 04b CNS and PNS
[view large image]
cord is filled with a mass of nerve cell bodies called gray matter. Each spinal nerve emerges from the spinal cord as two short branches, the dorsal and the ventral roots. These roots join just before the nerve leaves the vertebral column.
[Top]
Peripheral Nervous System
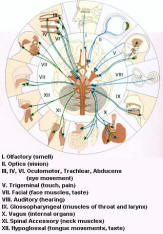
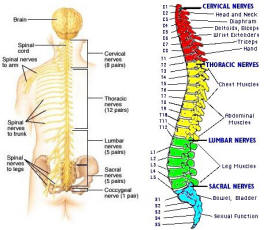
The peripheral nervous system is outside the CNS. It consists of the various nerves that connect particular parts of the CNS with particular organs. Humans have 12 pairs of cranial nerves and 31 pairs of spinal nerves. Cranial nerves (Figure 05) are either sensory nerves, motor nerves, or mixed nerves. All of them, except the vagus nerve, control the head, the face, the neck, and the shoulders. The vagus nerve controls the internal organs. Table 03 lists the functions of the various cranial nerves. All spinal nerves (Figure 06) are mixed nerves that take impulses to and from the spinal cord. Table 04
Figure 05 Cranial Nerves [view large image]
Figure 06 Spinal Nerves
[view large image]
describes the symptom of spinal cord injury (SCI) with the particular spinal nerve(s).
Continue to next page the Cranial Nerves
Return to brain page