What is in your food
Sat, 31 May 2008 17:55:07
Guide to treatment of Scleroderma
Scleroderma CREST guide
return
to Main page of scleroderma
Autoimmune diseases read our e-book If the disease started after a flu its
autoimmune.
The formation of calcium deposits in the connective tissues, which can be detected by x ray. They are typically found on the fingers, hands, face, and trunk and on the skin above elbows and knees. When the deposits break through the skin, painful ulcers can result.
Diffuse cutaneous scleroderma: This condition typically comes on suddenly. Skin thickening begins in the hands and spreads quickly and over much of the body, affecting the hands, face, upper arms, upper legs, chest, and stomach in a symmetrical fashion (for example, if one arm or one side of the trunk is affected, the other is also affected). Some people may have more area of their skin affected than others. Internally, it can damage key organs such as the intestines, lungs, heart, and kidneys. People with diffuse disease often are tired, lose appetite and weight, and have joint swelling and/or pain. Skin changes can cause the skin to swell, appear shiny, and feel tight and itchy. The damage of diffuse scleroderma typically occurs over a few years. After the first 3 to 5 years, people with diffuse disease often enter a stable phase lasting for varying lengths of time. During this phase, symptoms subside: joint pain eases, fatigue lessens, and appetite returns. Progressive skin thickening and organ damage decrease. Gradually, however, the skin may begin to soften, which tends to occur in reverse order of the thickening process: the last areas thickened are the first to begin softening. Some patients' skin returns to a somewhat normal state, while other patients are left with thin, fragile skin without hair or sweat glands. Serious new damage to the heart, lungs, or kidneys is unlikely to occur, although patients are left with whatever damage they have in specific organs. People with diffuse scleroderma face the most serious long-term outlook if they develop severe kidney, lung, digestive, or heart problems. Fortunately, less than onethird of patients with diffuse disease develop these severe problems. Early diagnosis and continual and careful monitoring are important.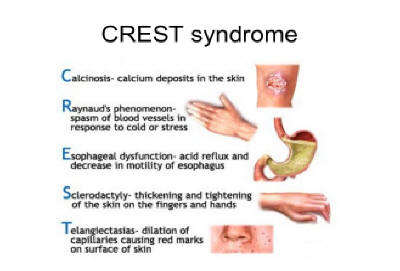
Calcinosis (KAL-sin-OH-sis):