Acute renal failurAcute renal failure in patients with congestive heart failure occurs because of decreased renal blood flow. This decrease is due to hypovolemia from overdiuresis or hypervolemia that causes elevated filling pressures of the left ventricle and leads to decreased cardiac output. Patients in the former group may respond to the discontinuation of diuretics and gentle hydration. Patients in the latter group are treated with diuretics and may need inotropes and vasodilators. Invasive hemodynamic monitoring may be required for fluid management.
CIDPUSA.org |
Intrinsic Acute Renal Failure
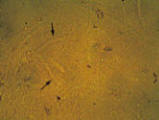
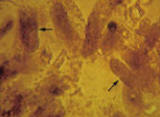
FIGURE 3. Hyaline and granular casts seen on urine microscopy. (Left) Hyaline casts (arrows). (Right) Granular casts (arrows). |
Patients at risk for acute tubular necrosis include those with diabetes, congestive heart failure or chronic renal insufficiency. Acute tubular necrosis may be prevented by promptly treating patients with reversible causes of ischemic or prerenal acute renal failure and by maintaining appropriate hydration in patients who are receiving nephrotoxins.
Once acute tubular necrosis develops, therapy is supportive. Drugs such as mannitol, loop diuretics, dopamine and calcium channel blockers have been somewhat successful in promoting diuresis in animals, but similar results have not been obtained in humans.
|