Nerve physiology
Impulse conduction - an impulse is simply the movement - an impulse is simply the movement of action potentials along a nerve cell. Action potentials are localized (only affect a small area of nerve cell membrane). So, when one occurs, only a small area of membrane depolarizes (or 'reverses' potential). As a result, for a split second, areas of membrane adjacent to each other have opposite charges (the depolarized membrane is negative on the outside & positive on the inside, while the adjacent areas are still positive on the outside and negative on the inside). An electrical circuit (or 'mini-circuit') develops between these oppositely-charged areas (or, in other words, electrons flow between these areas). This 'mini-circuit' stimulates the adjacent area and, therefore, an action potential occurs. This process repeats itself and action potentials move down the nerve cell membrane. This 'movement' of action potentials is called an impulse.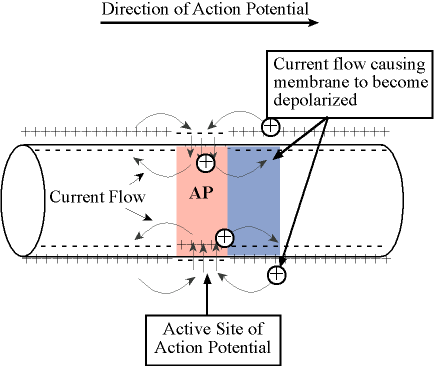
Please continue to next page of salutatory conduction
-
- CIDP DIAGNOSIS
- Treatment CIDP
- M.M.N. Multifocal Motor neuropathy
- Metal toxicity and learning
- Vitamin-C
- Vitamin -D deficiency and death
- Lymes disease with fatigue, joint pain and stiffness
- Axonal EMG , Multifocal motor neuropathy Electro Myography
- Painful neuropathy
Autoimmune cause
Key words : action, potential, nerve, membrane, depolarizes, negative, electron;