What is diabetes?
Autoimmune diabetes
What is diabetes?
Diabetes is a serious disease, which, if not controlled, can be life threatening. It is often associated with long-term complications that can affect every system and part of the body. Diabetes can contribute to eye disorders and blindness, heart disease, stroke, kidney failure, amputation, and nerve damage. It can affect pregnancy and cause birth defects, as well.
According to the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases (NIDDK) and the American Diabetes Association, diabetes affects an estimated 15.7 million people in the United States.
There are three main main types of diabetes that require clinical care by a physician or other healthcare professional:
- type 1 diabetes
- type 2 diabetes
- gestational diabetes
-
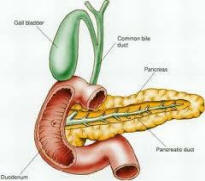
What is type 1 diabetes (diabetes mellitus)?
Type 1 diabetes is also known as diabetes mellitus, insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus (IDDM), juvenile diabetes, brittle diabetes, or sugar diabetes. There are two forms of type 1 diabetes:
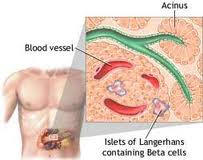
- idiopathic type 1 - used to refers to rare forms of the disease with no known cause, recently it has been learned it is caused by RotaVirus infection.
- immune-mediated diabetes - an autoimmune disorder in which the body's immune system destroys, or attempts to destroy, the cells in the pancreas that produce insulin. Immune-mediated diabetes is the most common form of type 1 diabetes.
What causes type 1 diabetes (diabetes mellitus)?
The cause of type 1 diabetes is rotavirus, enterovirus studies are provided below at the end of this page.
This auto-immune disease results from the body's failure to produce insulin, the hormone that allows glucose to enter the cells of the body to provide fuel. This is the result of an autoimmune process in which the body's immune system attacks and destroys the insulin producing cells of the pancreas.
When glucose cannot enter the cells, it builds up in the blood and the body's cells literally starve to death. People with type 1 diabetes must take daily insulin injections and regularly monitor their blood sugar levels.
What are the signs and symptoms of type 1 diabetes?
The following are the most common symptoms for type 1 diabetes, however, each individual may experience symptoms differently.
Type 1 diabetes often appears suddenly, and signs and symptoms may include:
- high levels of sugar in the blood when tested
- high levels of sugar in the urine when tested
- unusual thirst
- frequent urination
- extreme hunger but loss of weight
- blurred vision
- nausea and vomiting
- extreme weakness and tiredness
- irritability and mood changes
In children, symptoms may be similar to those of having the flu.
The symptoms of type 1 diabetes may resemble other conditions or medical problems. Consult your physician for a diagnosis.
Please go to the next page for the diagnosis and treatment of autoimmune diabetese